Ron Stultz
"Hydronic Heating System - Normal System Operation"
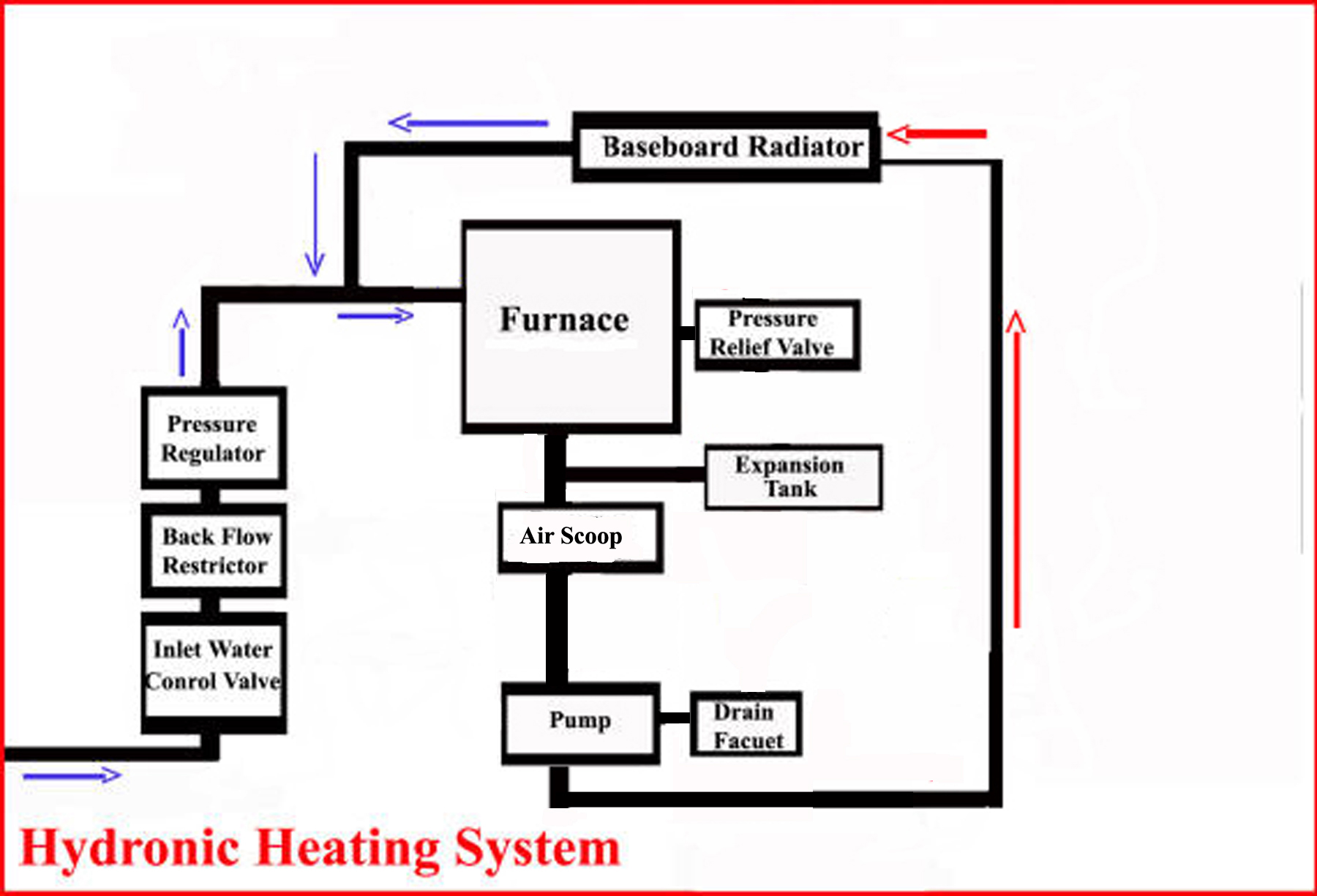
A hydronic heating systems works normally as follows:
- Power is supplied to the furnace via a circuit breaker in the circuit breaker panel and then through a power switch at or on the furnace.



- A thermostat is switched to "heat" and set at a temperature above current floor temperature.

- The thermostat that has been set to heat and at a temperature above current temperature, commands the control unit on or near the furnace to begin heating.

- The control unit commands the zone control valve for the floor demanding heat to open.
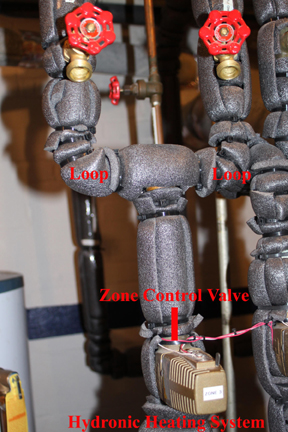
- The control unit commands the circulator pump to begin circulating water.

- If the water temperature at the control unit is above a fixed value, the control unit does nothing but let water circulate in the system. This condition occurs when the system has just heated water for another zone and there is residual heat left from the last heating cycle. Note here that a hydronic heating system does not keep water in the system hot all the time. For example, if all thermostats are set to a very low temperature, such as when the house is vacate, the temperature in the hydronic system can fall to ambient air temperature. The system will not start a heat cycle until a thermostat demands heat.

- If a thermostate demands heat and the water temperature at the control unit is below a fixed temperature. the control unit begins a water heating sequence (this preset temperature on my control unit is 150 degrees fahrenheit):
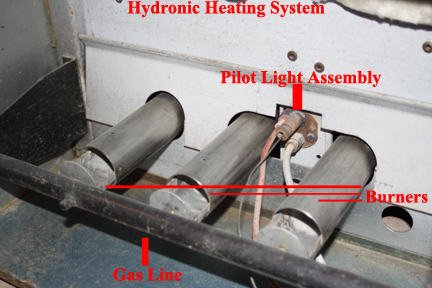
- The control unit commands the gas control unit to supply gas to the pilot light assembly.
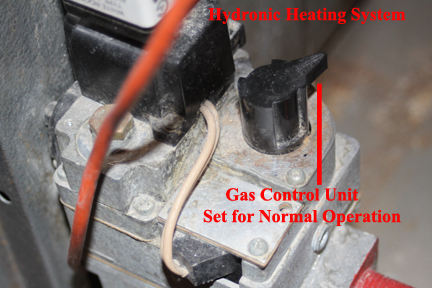
- The control unit supplies power to the pilot light igniter, which begins to spark right in the flow of pilot light gas, igniting the pilot light.

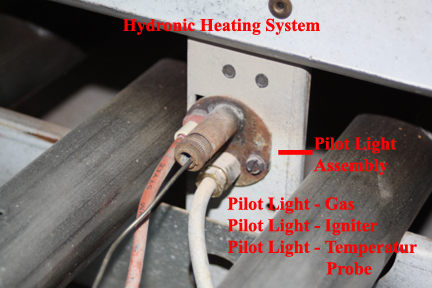
- If the pilot light actually starts burning, a thermocouple or temperature sensor. in the flow of the pilot light begins to heat up.
- At a preset temperature, the thermocouple or temperature probe tells the gas control unit to begin supplying gas to the furnace burners. Note here that if the pilot light does not ignite or if the thermocouple is not precisely in the flame of the pilot light or the thermocouple is defective, the system will never supply fuel to the burners.
- Furnace burners ignite off the pilot light and water heating begins.
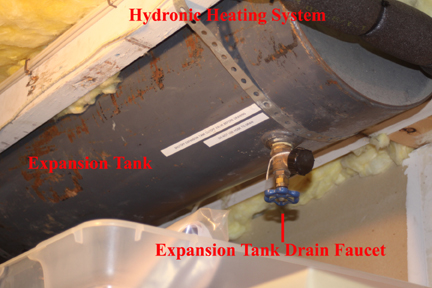
- As water is heated and circulated, water begins to expand from the heat. It is the role of the expansion tank to absorb the additional pressure resulting from heating. The expansion tank is filled with system water but has an air gap above the water level. As air compresses easier than water, additional water pressure compresses the air in the expansion tank. (My system has a cold water pressure of 18 pounds per square inch) and never rises above 20 PSI when heated.) If is important to properly drain your expansion tank before each heating season.

- When the water temperature at the control unit reaches a preset maximum, the control unit commands the gas control unit to stop gas flow to the burners. (My system control unit shuts down heating when the water temperature reaches 180 degrees farenheit.)
- If the thermostat that initially requested heat is still demanding heat, the control unit leaves the zone control valve open and continues to run the circulator pump. Should the water temperature at the control unit fall below the fixed lower temperature setting, the control unit begins another water heat cycle.
- When the air temperature on the floor or in the room where the thermostat that initially demanded heat. reaches the desired thermostat temperature, the thermostat stops calling for heat.
- The control unit recognizes that there is no current call for heat and it shuts down the circulator pump and then the applicable zone valve.
- Finally note, that during the water heating cycle, should the water pressure exceed the pressure relief valve set pressure, the pressure relief valve will dump water, reducing system pressure (the pressure relief valve does reduce system pressure but if the water inlet valve is set to too high a pressure, the water inlet valve will begin filling the system with more water and again creating an over pressure situation.)
